Asherman’s Syndrome is when the lining of the womb becomes scarred. This scar tissue is often called intra-uterine adhesions or synechiae. In many cases the front and back wall of the womb are stuck together. So, what causes Asherman's Syndrome, how do you know if you've got it and can you get pregnant if you have it? We have the answers to all your questions.
What causes Asherman's Syndrome?
Asherman’s is usually caused by trauma to the womb lining and 9 out of 10 cases are after surgical termination of pregnancy or surgery to treat miscarriage. After one termination the risk of Asherman’s is 16%, however, after 3 or more surgical procedures, the risk increases to 32%.1 Nevertheless, Asherman’s can occur after a retained placenta or caesarean birth. Although not common in developed countries, genital tuberculosis and other infections can also cause scarring.
How to spot Asherman's Syndrome
Many women with Asherman’s will present with a change in periods such as having much lighter periods after surgical treatment. Nonetheless, some women will still continue to have normal periods.
Diagnosing Asherman's Syndrome
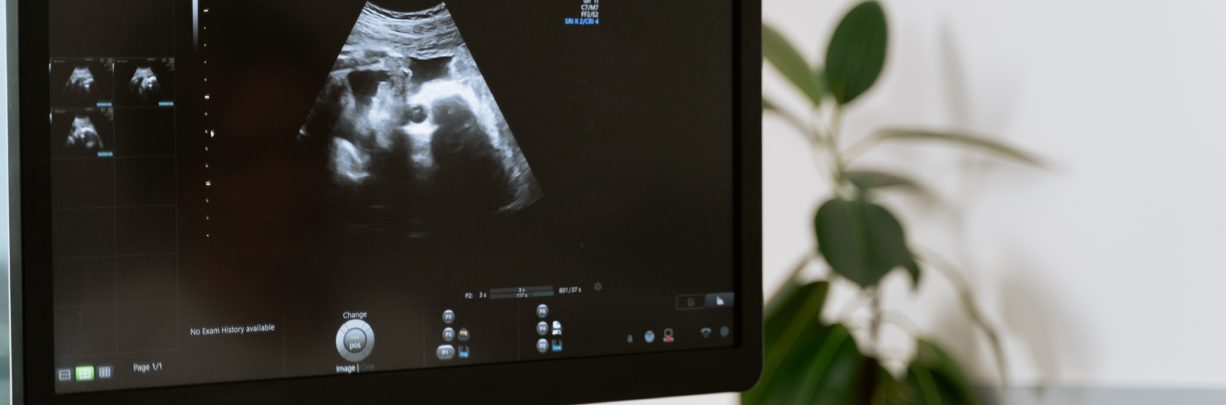
A thin endometrium on ultrasound scan can suggest Asherman’s, but the best test is a hysteroscopy where a small camera is passed inside the womb.
Treatment for Asherman's Syndrome
Asherman's Syndrome must be treated by a very experienced surgeon via hysteroscopy. Research suggests that using small scissors to separate the adhesions is less likely to cause more damage than using electrosurgery or laser which causes heat and can potentially lead to more scarring.
Very few surgeons are experienced in treating this condition, so useful questions to ask are about the technique the use: scissors or other device, and how many patients they have treated previously. This type of surgery is usually performed under general anaesthesia.
After surgery
Frequently, surgeons will prescribe estrogen after the operation in an attempt to thicken the lining of the womb to prevent scar tissue from re-forming. Others will leave a small balloon or a coil. No good evidence exists to support the use of these additional treatments, but as the condition is so rare, it is difficult to carry out research in this area.
What are the chances of having a baby?
A recent study of the reproductive outcomes for women after surgical management for Asherman’s Syndrome looked at 500 women who were followed up for at least two years after surgery. In total, 569 pregnancies were achieved within 3 years after surgery. The miscarriage rate was 33.0%, which is a little higher than for women without Asherman’s. The live birth rate was 67.4%.
Women with the best chances of having a baby tended to be:
- Younger.
- Asherman’s caused by a surgical termination of pregnancy or management of miscarriage in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Low grades of adhesions.
- No miscarriage after adhesiolysis.
Getting support for Asherman's Syndrome
Little is written about Asherman’s syndrome online and few research studies have been done to be able to provide clear advice. Therefore it’s essential to see a specialist who understands the condition and it’s treatment but also consider you as a whole person.
For further information, check out our other content on trying to conceive, pregnancy and wellbeing.
Sign up today for unlimited access:
- Book appointments
- Expert advice & tips
- Premium videos & audio
- Curated parenting newsletters
- Chat with your bloss community
- Discounts & competitions
- Special events

Leave a Rating / Review
You must be logged in to post a comment.